Terminology
Our next order of business: terminology. If you don’t understand the terms you’ll never understand the process.

User Interface and Experience
Graphical User Interface (GUI): The interface through which users interact with digital devices or applications.
Information Design: The practice of presenting information in a way that fosters an efficient and effective understanding of it.
User Interface (UI): The interaction interface between users and digital devices or software.
User Experience (UX): The overall event associated with using a digital product, focusing on its usability and the pleasure it provides.
Design Principles
Alignment: The placement of elements in a design, creating a cohesive visual experience.
Atomic Design: A methodology composed of five distinct stages working together to create interface design systems in a more deliberate and hierarchical manner.
Balance: The distribution of visual weight in a design. It can be symmetrical or asymmetrical.
Contrast: The difference between two elements of a design.
Design Thinking: A problem-solving methodology that involves empathizing with users, defining user needs, ideating solutions, creating prototypes, and testing those solutions.
Hierarchy: The order of importance of elements in a design.
Mobile First Design: A design strategy that says websites should be designed for mobile first, then scaled up and adapted for larger screens.
Proximity: Grouping related items together to create a relationship between them in a design.
Typography: The art of arranging type to make the text legible and appealing to read.
White Space: Also known as ‘negative space’, this refers to the blank spaces in a design, which can help to highlight other elements.
Product Development
Design Sprint: A time-constrained, five-phase process that uses design thinking to reduce the risk when bringing a new product, service, or a feature to the market.
Minimal Viable Product (MVP): A product with enough features to satisfy early users, providing feedback for future development.
Product: A digital offering, such as a website or app, meant to fulfill a market need.
Prototype: A mock-up or demo of a website or app used to gather feedback and iteratively improve a design.
Storyboard: A visual representation of a user’s journey throughout a product, useful for planning new features or changes.
User Stories: Informal, natural language descriptions of one or more features of a software system. User stories are often written from the perspective of an end-user or user of a system.
Wireframe: A schematic or blueprint that represents the framework or structure of a website or app, showing the arrangement of content and functions.
Usability
Accessibility: The design of products, devices, services, or environments to be usable by as many people as possible, including those with disabilities.
Card Sorting: A method used to help design or evaluate the information architecture of a site. In a card sorting session, participants organize topics into categories that make sense to them and they may also help you label these groups.
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): The practice of increasing the percentage of users who complete a website’s desired action (like making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter).
Heuristics: Broadly accepted usability principles that guide the design process.
Responsiveness: A website’s ability to automatically adjust and adapt its layout based on the user’s screen size and device for optimum usability.
Usability Testing: A technique used in user-centered design to evaluate a product by testing it on users. This can provide direct input on how real users use the system.
User Flow: The path taken by a user on a website or application to complete a task, such as buying a product.
Customer Interaction
Customer Journey Map (CJM): A visual narrative of customer interactions with a brand, from initial engagement through long-term value.
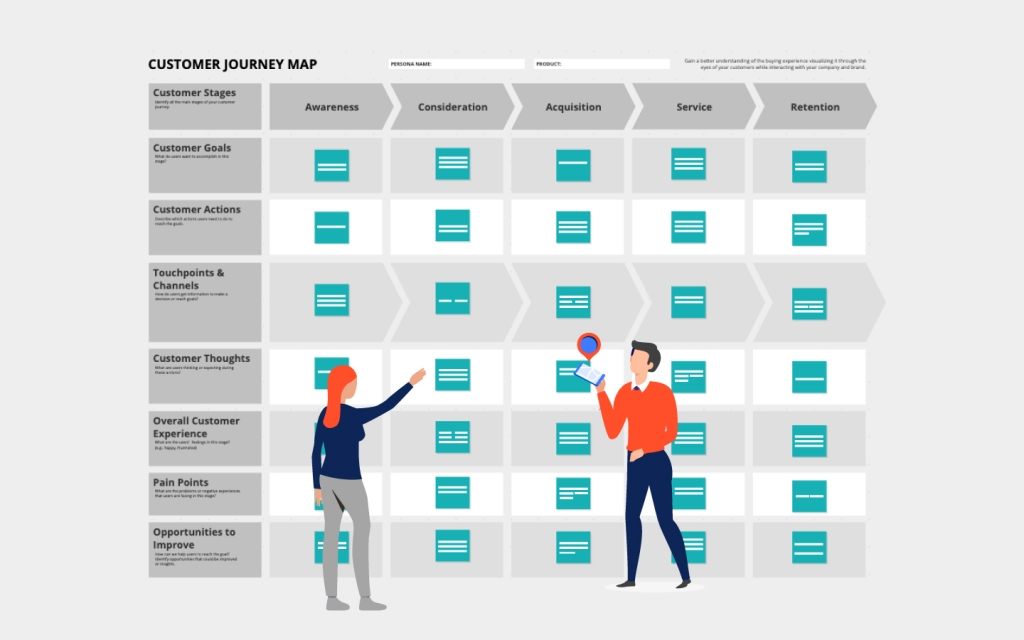
User Persona: A semi-fictional character based on your target audience data, which represents a major user group for your website or product.
Design Aspects
Color Gradient: The blending of one color into another, creating a new color.
Color Converter: A tool that converts colors from one data type to another (RGB, CMYK, PMS, HEX).
Control Elements: Changeable design elements required for coding the new interface, like buttons or sliders.
Flat Colors: Solid colors without gradients, screens, or halftones.
Material Design: A color system that assists in creating brand-related color schemes.

Swiss Colors: A digital tool for finding inspiring color combinations.
Content Strategy Terms
Information Architecture (IA): The structural design of shared information environments; the art and science of organizing and labeling websites, intranets, online communities and software to support usability and findability.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): The practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results.
Quality Assurance and Control
A/B Testing: A method of comparing two versions of a webpage or other user experience to see which one performs better.
Quality Assurance (QA): Activities that monitor and verify processes used to manage and create deliverables, aimed at preventing defects.
Quality Control: A process that verifies if the desired quality has been achieved, aiming to identify and correct defects.
Branding and User Perception
Branding: Features that identify a seller’s goods or services.
Quality Attribute (QA): Product characteristics as judged by users, including reliability, functionality, usability, efficiency, and portability.
Web Development Terms
Agile Development: A set of practices intended to improve the effectiveness of software development and project management. Agile methods emphasize flexibility, iterative progress, and customer feedback.
API (Application Programming Interface): A set of rules and protocols for building and interacting with software applications.
Back-End: The part of a website users do not see. It is the tech behind the scenes, making the website work.
Bootstrap: A free and open-source CSS framework directed at responsive, mobile-first front-end web development. It contains CSS and (optionally) JavaScript-based design templates for typography, forms, buttons, navigation, and other interface components.
Content Management System (CMS): A system used to manage the creation and modification of digital content.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): A style sheet language used for describing the look and formatting of a document written in HTML.
Database: A structured set of data. In web development, databases are often used to store website data like user information, page content, etc.
Front-End: The part of the website users interact with. It includes everything that you see when navigating around the Internet.
Figma: A cloud-based design tool that is similar to Sketch in functionality with the added feature that it allows for real-time collaboration.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): The standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications.
JavaScript: A high-level, interpreted programming language that is a core technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS.
jQuery: A fast, small, and feature-rich JavaScript library. It makes things like HTML document traversal and manipulation, event handling, and animation much simpler with an easy-to-use API that works across a multitude of browsers.
Responsive Web Design (RWD): An approach to web design that makes web pages render well on a variety of devices and window or screen sizes.
Server: A computer program or device that provides functionality for other programs or devices, called “clients”.
Scrum: A framework within which people can address complex adaptive problems, while productively and creatively delivering products of the highest possible value. Scrum is often used in Agile Development.
Sprint: A set period of time during which specific work has to be completed and made ready for review (commonly used in Agile Development).